Can You Read Engine Rpm's With a Lab Scope
Performing a polish running examination

Workings of a smooth running examination
Many factors are contributing for an engine to be running smoothly and producing the desired corporeality of power. Mechanical components, electronical components and a correct performance ECU are the main factors. When an engine is non running properly, a smooth running examination can be performed to check if the main functions are working correctly. A smooth running test is done on engines that run troublesome, misfire or have erratic faults at certain RPMs.
A smooth running examination is a measurement on the main inputs and outputs to diagnose if they are working properly. The main inputs are the crankshaft and camshaft sensors and master outputs are the injection en ignition signals. The crankshaft and camshaft sensors are position sensors used past the ECU to decide the position and the speed of the engine to adjust the output signals accordingly. The smooth running test tin can be used to cheque the camshaft and crankshaft timing, which tin can change due to a stretched or slipped timing belt or chain. Besides the crankshaft and camshaft sensor, the ECU uses signals of the coolant temperature sensor, mass air flow sensor and more than sensors to determine the injection and ignition timing.
This measurement is performed on a good running engine, on an inductive crankshaft sensor, an anterior camshaft sensor, an indirect injector and the trigger signal of the COP ignition. Details of every component can exist read in the private articles, this measurement is performed to show the relation betwixt these individual signals in a motor management system.
Connecting the lab scope
Performing a smooth running test tin be done past measuring the crankshaft sensor, the camshaft sensor, the injection actuator and the ignition actuator point voltages, see figure ane:
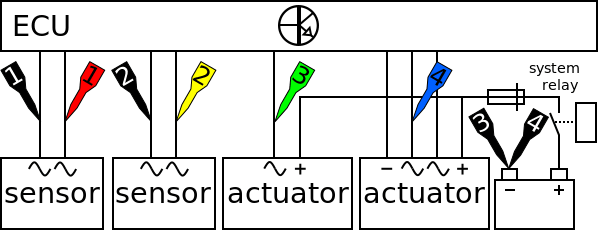

The lab telescopic is connected to the crankshaft sensor, camshaft sensor, injection signal and ignition signal via a Measure lead TP-C1812B and Back Probe TP-BP85 and set to is set to normal scope fashion.
Measuring
Figure 3 shows waveforms of the crankshaft sensor, the camshaft sensor, the injector and the ignition of an engine running at idle speed. This betoken can be downloaded and used to correctly gear up the lab telescopic or as reference signal.
Download smooth running exam measurement at idle speed
Download smooth running test measurement at 1800 RPM
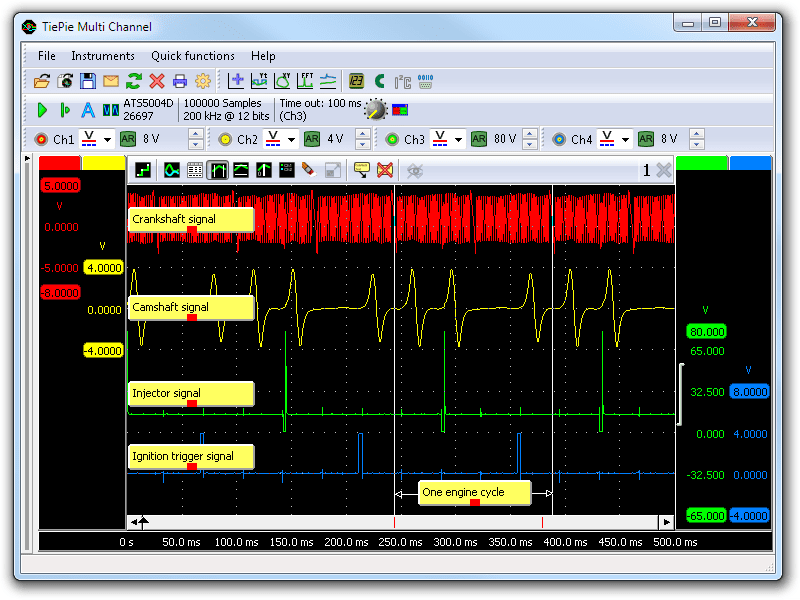
The following measured signals are shown:
- channel ane (carmine) shows the crankshaft sensor signal
- channel 2 (yellow) shows the camshaft sensor signal
- channel three (green) shows the injection signal
- aqueduct 4 (blue) shows the ignition trigger signal
One engine cycle, indicated in the bottom of the graph, contains 2 rotations of the crankshaft (visible by two sequential waveform patterns in the crankshaft point) and one camshaft rotation (visible past a unmarried waveform design). The ignition trigger signal has a rising edge which activates the COP ignition and the falling edge is the bodily time when the ignition has to have identify. During one engine wheel the injection take place at TDC (meridian dead center) when the intake stroke is starting. After this the pinch stroke takes identify and only earlier the side by side TDC an ignition takes place.
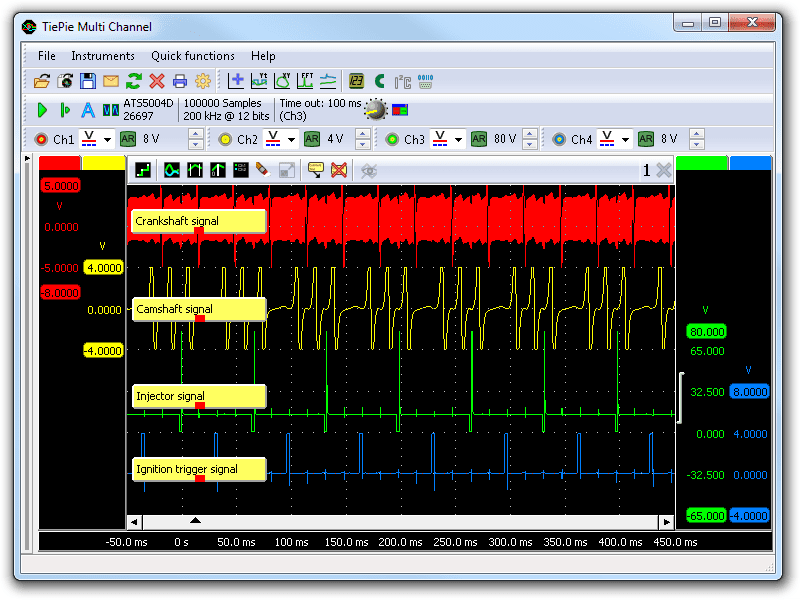
Figure 4 shows the same measurement with raised engine speed to 1800 RPM. The smooth running examination is setup to measure the aforementioned signals at college engine speeds. With the raised engine speed faults can show up, for case malfunctioning crankshaft sensor or camshaft sensor signals or missing injections or ignitions causing misfires.
When erratic or intermittent faults occur the intermittent fault measurement can be performed with the labscope still continued every bit in this measurement, using the settings described in the intermittent fault measurement applied.
Diagnosis
RELATED PRODUCTS
RELATED Articles
- inductive crankshaft sensor
- With a lab scope an inductive crankshaft sensor is measured during cranking of an engine, as well every bit during idling. The signal from the sensor is shown and tin be downloaded. To aid determining whether an inductive crankshaft sensor is functioning correctly, different possible deviations from the example signal are mentioned along with probable causes.
- Camshaft sensor inductive
- With a lab scope an inductive camshaft sensor is measured during cranking of an engine, likewise as during idling. The indicate from the sensor is shown and tin be downloaded. To assist determining whether an inductive camshaft sensor is operation correctly, different possible deviations from the example signal are mentioned forth with probable causes.
- Indirect injection voltage measurement
- A lab scope is used to measure an injector bespeak voltage on an idling engine at operating temperature. The signal from the sensor is shown and tin can exist downloaded. To help determining whether the injector is functioning correctly, different possible deviations from the example signal are mentioned along with possible causes.
- COP ignition measurement
- With a lab scope a COP ignition is measured with a Scroll-on-Plug probe TP-COP750. The betoken from the COP ignition is shown and tin can be downloaded. To help determining whether the COP ignition is functioning correctly, unlike deviations from the case signal are mentioned forth with possible causes.
Disclaimer
This document is subject to changes without notification. All rights reserved.
The information in this awarding note is carefully checked and is considered to be reliable, yet TiePie engineering assumes no responsibleness for any inaccuracies.
Safety warning:
mitchellcatir1937.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.tiepie-automotive.com/en/articles/smooth-running-test
0 Response to "Can You Read Engine Rpm's With a Lab Scope"
Post a Comment